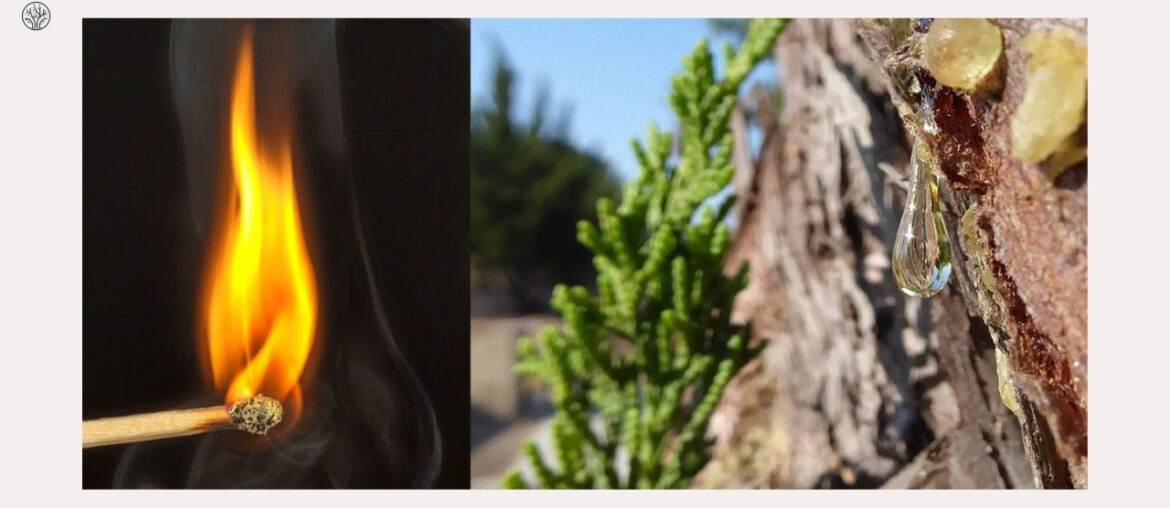
Is tree sap flammable?
The short answer is yes. For centuries, tree sap, or resin, has been known to be highly explosive and flammable. However, the extent of its flammability and its uses may surprise you.
In this guide, we’ll explore this topic in more depth, including how to test it, its practical uses, and safety precautions. Whether you’re a nature enthusiast, a survivalist, or simply curious about tree sap, we will give you the knowledge you need to understand and harness this fiery potential.
How To Test The Flammability Of Tree Sap?
Tree sap consists of a mixture of water, sugar, minerals, and various organic compounds, all of which can be flammable. Therefore, the resin can readily ignite and burn rapidly.
However, it’s crucial to note that not all tree sap is equally flammable. Some tree species produce sap with higher sugar content, making it more prone to ignite quickly. For example, pine tree sap, with its resinous and sticky nature, is known for its high flammability. In contrast, the sap from some trees, like oak or elm, is less flammable.
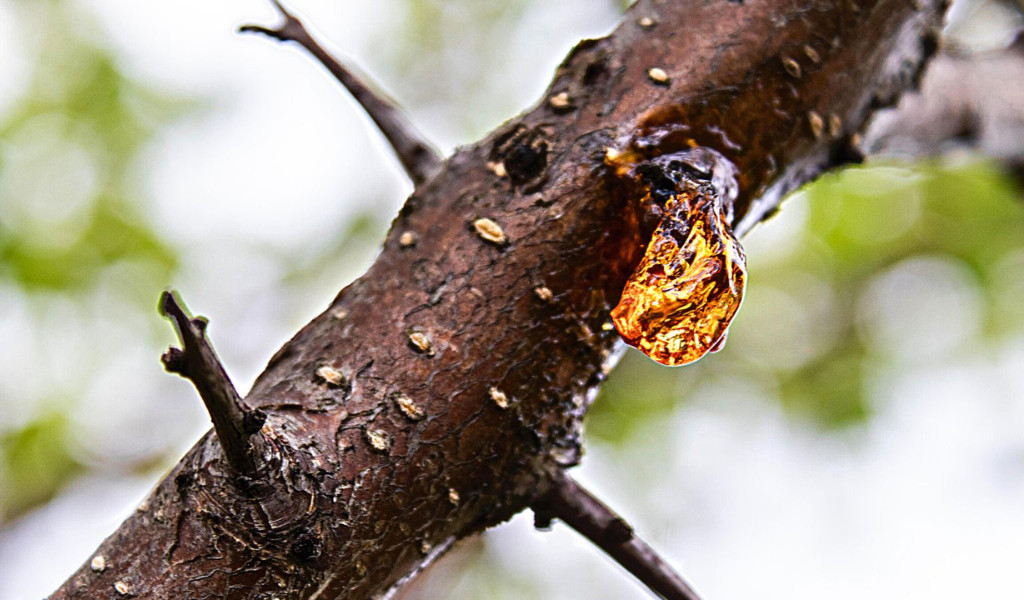

There’s a simple way to test how flammable tree sap is. Follow these steps:
- First, gather a small amount of tree sap, preferably from a pine tree. Pine tree sap, in particular, is renowned for its high flammability and has been used for centuries to start fires in various applications.
- Then, find a safe and well-ventilated area, away from flammable materials, and use a small heat source, like a lighter or a match, to expose the sap to a flame.
- If the sap ignites easily and burns with a steady flame, it indicates its flammability. Remember that tree species produce sap with varying flammability levels, so the results may differ.
It’s essential to use extreme caution during this test to avoid accidents. Ensure you have a fire extinguisher or a container of water nearby to extinguish the flame quickly if it becomes uncontrollable.
See more: Why do most leaves appear green?
Practical Uses Of Flammable Tree Sap
While the question ‘Is tree sap flammable?’ may raise concerns, its practical applications have been used for generations.
Traditional Uses
Before the age of industrialization, our ancestors found numerous practical uses for flammable tree sap:
- Starting fires: The flammability of tree sap made it an invaluable resource for starting fires. By applying a small amount of sap to kindling or a fire starter, one could ignite a fire quickly and efficiently. Many from different cultures have used this traditional method throughout history.
- Waterproofing: The resinous nature of tree sap made it an excellent waterproofing material. Ancient civilizations used tree sap to seal the seams of boats and canoes, preventing water from entering. It was also applied to clothing and tents to create a waterproof barrier.
- Healing ointment: Some cultures used tree sap as a healing ointment for wounds. The antiseptic properties of sap helped prevent infection and promote the healing process. It acted as a natural protective barrier against bacteria and other contaminants.
For your information, the sap from Eucalyptus trees serves as more than just a natural remedy for wound care; it’s a superb antiseptic because of its antibacterial and antifungal qualities. This feature makes it especially helpful in managing skin prone to acne, as it can aid in reducing inflammation and redness.
Modern Applications

In the current world, tree sap’s flammability finds utility in several industries:
- Varnishes and adhesives: Tree sap is a crucial component in producing varnishes and adhesives. Its sticky and durable nature makes it an ideal binding agent. When combined with other chemicals, it can create glossy finishes for wood and other surfaces.
- Perfumes and fragrances: Some perfumes and fragrances contain tree sap, particularly resins, to enhance their scents. The resinous aroma adds depth and complexity to various perfumes, providing a unique olfactory experience.
- Maple syrup making: Maple syrup is an extract from the sap of maple trees. It results from a fascinating process known as sugaring or maple sugaring. This sweet and flavorful syrup is renowned for its unique taste and has become a common sweetener in cooking.
- Turpentine production: Turpentine is a solvent derived from the resin of pine trees. It has many applications, including as a solvent in the paint and varnish industries. Turpentine’s ability to dissolve substances makes it invaluable in various chemical processes.
And there are many more applications of tree sap. Whether in the production of everyday products or as a valuable tool for outdoor enthusiasts, tree sap plays a vital role in various aspects of our lives. Understanding the versatile and practical uses of flammable tree sap not only sheds light on its historical value but also highlights its relevance in today’s world.
Is Burning Tree Sap Toxic?
In a forest with resinous trees, the question ‘Is burning pine sap toxic?’ becomes a critical safety concern. While tree sap itself is generally not toxic, the act of burning it can introduce potential hazards. Here’s a closer look at why and how burning tree sap can be a concern:
When tree sap is burned, volatile organic compounds (VOCs) are released into the air. These chemicals can be harmful when inhaled, leading to respiratory issues and, in some cases, long-term health problems. High concentrations of VOCs can even contribute to indoor air pollution if you’re burning tree sap in an enclosed space.
Apart from VOCs, the explosion of tree sap can produce other harmful substances like carbon monoxide and soot. Both can be hazardous in a confined space and can result in respiratory issues or worsen existing conditions such as asthma. Moreover, these substances may pose risks when they come into contact with the skin.
But that’s not all: The heat from burning can alter the chemical composition of tree sap, potentially creating new compounds that may not have been present in the sap in its original form. Some of these compounds might be toxic or irritating.
Safety Measures To Take When Handling Flammable Tree Sap
- Ventilation: Whenever you’re using flammable tree sap, make sure you’re in a place with good airflow. It helps get rid of any fumes that might be harmful. Good ventilation is essential, especially when dealing with larger quantities of tree sap.
- Protective gear: When working with tree sap, wear gloves and safety goggles to keep your skin safe and your eyes shielded from splashes. Tree sap can be sticky, and it’s not easy to clean off, so remember to wear the right gear.
- Fire safety: Keep a fire extinguisher close when working with flammable tree sap. Accidents can happen, and you must prepare to put out any unexpected fires. Having a first aid kit around for minor injuries is a good idea, too.
- Storage: How you store tree sap makes a big difference. Put it in sealed containers to keep it as explosive as possible. Keep these containers away from anything hot or flames to avoid accidents.
- No ingestion: Never, ever eat or drink tree sap or let it touch your food or drinks. Some tree saps can be harmful or cause digestive discomfort if you swallow them. After handling tree sap, wash your hands well before eating or drinking anything to be safe.
These safety rules are crucial when you’re working with flammable tree sap. They help you stay safe and make sure your experience with this potentially tricky stuff is under control. Safety should always be a top priority when dealing with flammable materials.
How Tree Sap Can Cause Fires?
Tree sap, especially from certain species, can ignite under specific conditions. For instance, high temperatures play a significant role in making tree sap ignite more easily. On hot days or in the presence of heat sources, the sap may ignite more rapidly.
Also, mechanical activities, such as chopping wood, can generate sparks. When these sparks come into contact with flammable tree sap, they may trigger ignition.
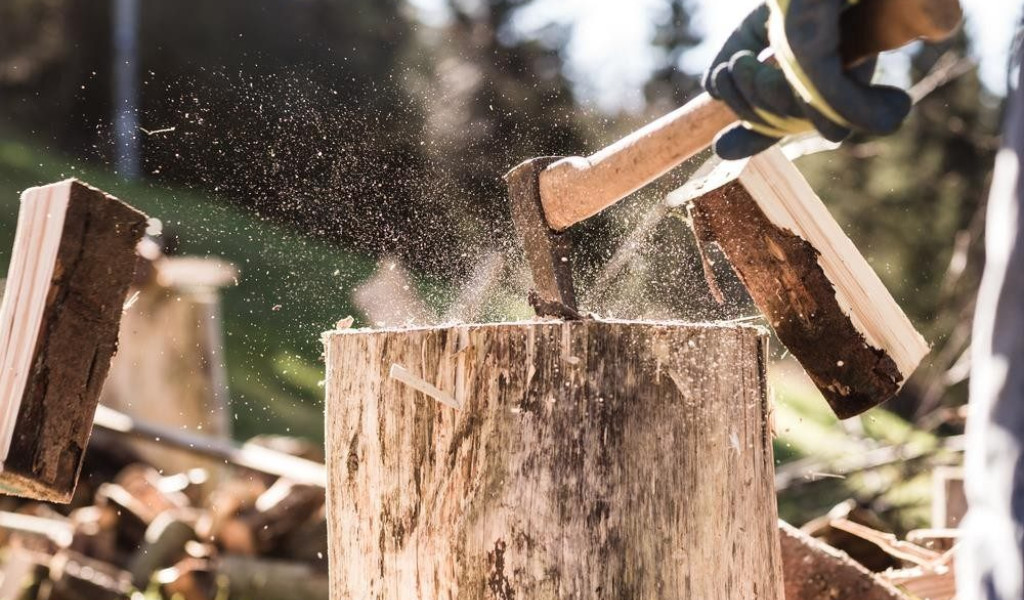

By being aware of these conditions, you can take precautions to reduce the risk of accidental fires when working with tree sap. Always handle flammable tree sap in well-ventilated areas, away from open flames or sparks, and have fire safety equipment readily available to ensure safe handling.
In a tree sap fire, remember to act swiftly and cautiously to ensure your safety and prevent the fire from spreading. Here’s what to do:
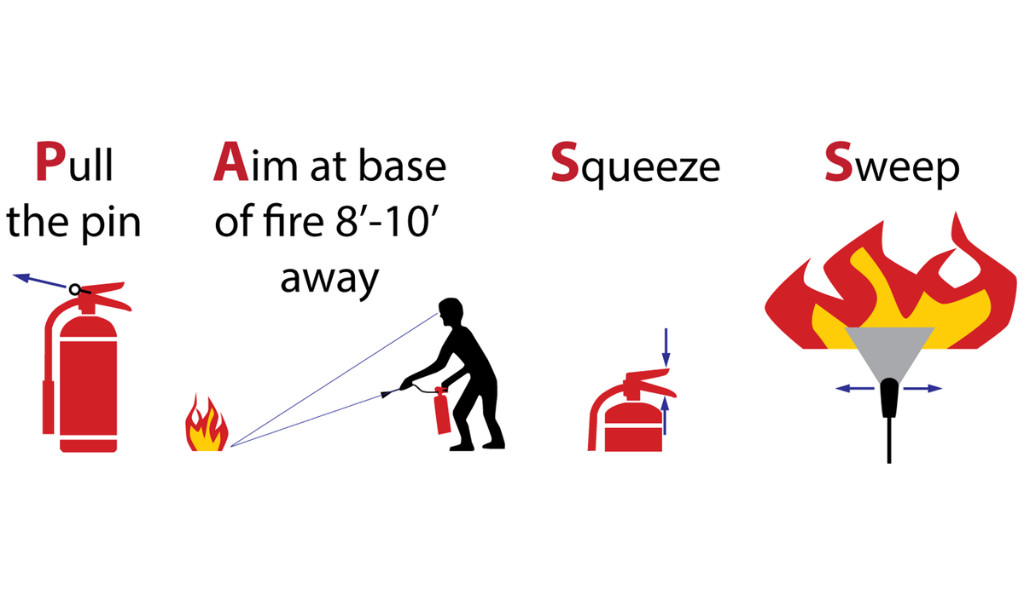
First, quickly evaluate the size and intensity of the fire. If it’s a small, manageable flame, consider handling it yourself. With a fire extinguisher on hand, you can use it to smother the flames. Aim the extinguisher at the base of the fire and sweep from side to side. Continue until the fire is entirely out.
However, if the fire is large or spreading rapidly, prioritize your safety and do not attempt to handle it alone. Evacuate the area, ensuring that everyone in the area does the same. Close doors behind you to contain the fire’s spread.
Then, contact emergency services (911 or the relevant local emergency number) to report the fire and request professional assistance. Provide them with your location and any crucial information about the fire.
Do not attempt to re-enter the area or tackle the fire again. Wait for the arrival of trained firefighters with the proper equipment and expertise to handle the situation safely.
Remember that safety should always be the top priority. It’s crucial to be prepared and have the necessary safety equipment and knowledge when working with flammable substances like tree sap to prevent accidents and respond effectively in the event of a fire.
FAQs
Why is pine tree sap highly flammable?
Pine tree sap is highly flammable due to its chemical composition. It contains volatile organic compounds (water, sugar, minerals, and more), making it easier to ignite when exposed to heat or flames. This flammability has made pine sap a valuable resource for kindling fires for centuries.
Is maple tree sap flammable?
While maple tree sap can be ignited, it is less flammable than pine sap. Maple sap has a lower resin content and a higher water content, which makes it less prone to rapid combustion. Many still use it to start fires, but it may require additional kindling.
Will sap burn your skin?
Tree sap is sticky and difficult to remove from the skin, but it is not inherently harmful. However, if you get tree sap on your skin and it catches fire, it can cause burns. It’s essential to take precautions when handling flammable tree sap to avoid accidents.
The Bottom Line
Now you have the answer to your question: Is tree sap flammable? Yes, it is indeed flammable, and its flammability varies depending on the tree species. While tree sap is a potential fire hazard, it is still a valuable resource with various practical applications throughout history. Don’t forget to check out our latest article: “What side of the tree does moss grow?” and follow us for more valuable insights on the natural world.









